Educating and Empowering You to Heal, Thrive, and Live a Happy, Healthy Lifestyle
Insulin Resistance and Diabetes
Insulin Resistance | Pre-diabetes | Diabetes | Diabesity (part 1)
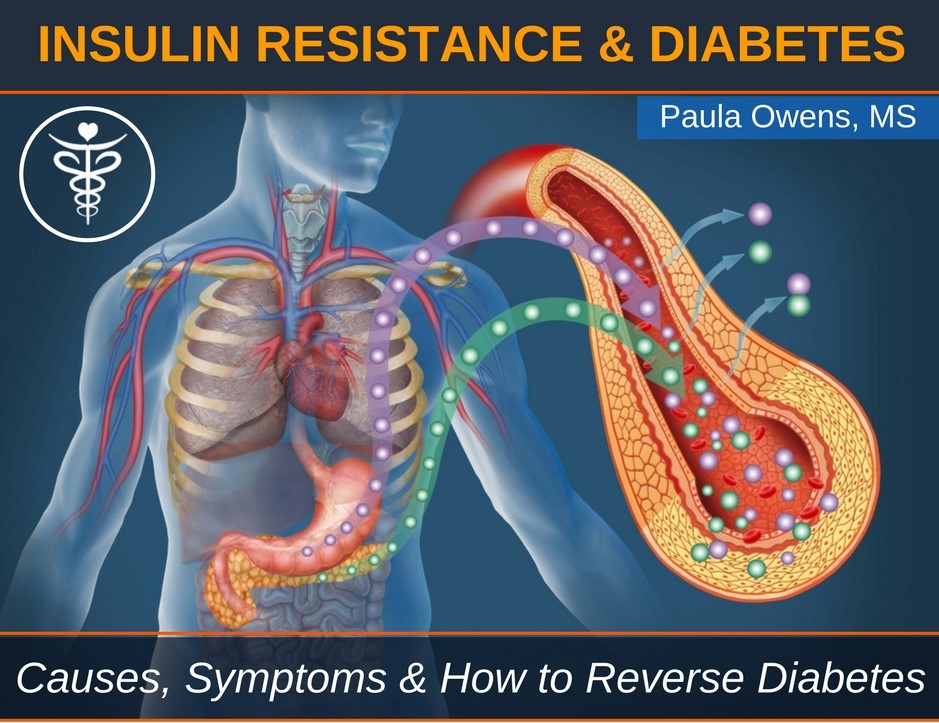
Insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, pre-diabetes and obesity (diabesity) are global epidemics that continue to rise resulting in major health problems and disease. Diabetes is a metabolic disorder affecting 400 million people worldwide. Approximately 1/3 of adult Americans are now obese; 2/3 are overweight; and diabetes afflicts approximately 29 million. Another 86 million Americans have pre-diabetes!
Insulin resistance, pre-diabetes and diabetes are lifestyle dis-eases that are preventable and reversible.
These metabolic conditions are caused by poor lifestyle choices, unhealthy food choice, eating too many chemicals, a high toxic load, exposure to blue light at night, pesticides, harmful chemicals, endocrine disruptors, underlying infections, chronic stress, and inactivity. There is also evidence of autoimmunity in type 2 diabetes.
If you think diabetes and insulin resistance affects only those who are overweight, are sugar and carb junkies, feast on junk food, and are sedentary, listen up.
According to the National Institute of Health, approximately 15% of those with insulin resistance and those diagnosed with type 2 diabetes are not overweight – they’re skinny on the outside, but fat on the inside commonly known as “skinny-fat.” On the inside at the cellular level, these folks have excessive visceral fat (intra-abdominal fat around organs), which is known to increase the risk of insulin resistance and diabetes.
Just because someone is thin, does not mean they’re healthy – a common misconception in our society.
A study by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development predicts that by 2020 nearly 75% of the American population will be overweight or obese. What does this mean? More than two-thirds of all Americans will be pre-diabetic or suffer with type 2 diabetes.
What is Insulin Resistance?
With insulin resistance, the normal amount of insulin secreted is not sufficient to move glucose into the cells and the the cells become “resistant” to the action of insulin. The cells loses its responsiveness on the insulin receptor site (particularly liver, muscle and fat cells, with the liver losing sensitivity first, followed by muscle, then fat cells). To compensate, the pancreas secretes more insulin to maintain fairly adequate blood-sugar movement into cells and a normal blood-sugar level.
To put it another way, think of insulin as a key that opens doors to the body’s cells, so glucose can enter. With insulin resistance, it’s like having locks that are frozen or rusty. The key won’t turn and glucose can’t get into the cell. This causes the pancreas to crank out more insulin to keep the level of glucose in the bloodstream from spiraling out of control. Eventually, the cells quit responding and you’re insulin resistant. If this continues, gradually the pancreas give up leading to type 2 diabetes.
In type 2 diabetes, your body isn’t making enough insulin or the cells are resistant to insulin. This causes too much sugar to build up and remain in the blood. Insulin takes the sugar from the blood into the cells.
Although insulin is necessary for your body’s use of metabolizing sugar, higher insulin levels (>10) accelerate the aging process, increase the risk of heart disease, dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and lead to diabetes, oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, excess inflammation, PCOS, estrogen dominance, and other hormone imbalances.
You want to create an environment in which you’re sensitive to insulin. Insulin sensitivity is your body’s ability to use insulin properly to regulate the amount of glucose in the bloodstream.
Optimal serum glucose fasting blood levels are 70-80. ‒ Harry Eidenier, Jr., Ph.D. Fasting blood sugars in the 70s are the most protective for prevention of cardiovascular disease and neurological decline. Abnormal blood sugar is anything over 95. Glucose levels between 80-95 are an opportunity to restore blood sugar back to an optimal range.
“If you measure your fasting blood sugar and it’s 95 and it should be 75, that’s a 20 point difference making it a 20% increased risk of heart attack. Every one point that your blood sugar is over 75 is a one percent increased risk of for heart attack.” ‒Mark Houston, MD
Fasting serum insulin levels should be <10. Longevity studies of all creatures from worms and yeasts to humans show that the lower the levels of insulin are over the course of a life, the longer the life will be. High insulin levels (>10) cause major oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation to your brain and body. The most recognized of these is diabetes, but that is far from the only problematic disease.
“It doesn’t matter what disease you are talking about, whether you are talking about a common cold or cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis or cancer, the root is always going to be at the molecular and cellular level, and I will tell you that INSULIN is going to have its hand in it, if not totally control it.” —Ron Rosedale, M.D.
Insulin resistance, high blood sugar, pre-diabetes and diabetes are significant players in the risk of dementia and cognitive dysfunction. Diabetes (and high blood pressure) in middle age (age 40-64) leads to brain cell loss, dementia, problems with memory, thinking skills, hormone imbalances, and other damage to the brain later in life.
Insulin Resistance
Diabetes is linked to dementia and cognitive dysfunction
Published in the journal Neurology, researchers evaluated the size of the brain’s memory center, the hippocampus, using a specialized type of MRI scanner. They measured the blood glucose levels in the same individuals. When the data was analyzed, a direct relationship was found between the degree of atrophy or shrinkage of the hippocampus and blood sugar measurements. Even subtle elevations of blood sugar (far below the level where one would be labeled as being diabetic) were already associated with brain shrinkage. What’s more, the researchers also performed cognitive testing on these individuals and found a direct relationship between failing memory and blood sugar elevation.
The take home message here is straightforward: Even mild elevations of blood sugar correlate perfectly with both brain degeneration and cognitive dysfunction. And because your blood sugar directly reflects your sugar and carbohydrate consumption, you can choose to directly influence the size, and more importantly the preservation of function of your brain by balancing your blood sugar and insulin.
Be smart, obtain annual lab tests and Balance your Body Chemistry with a Functional Blood Chemistry Analysis.
Red flags: fasting glucose >95, HbA1C >5.7, low vitamin D and elevated triglycerides are early warning signs that you’re not metabolizing sugars adequately, a pre-diabetic environment and could soon develop diabetes. Other red flags include a low HDL, increased uric acid, increased CRP, fibrinogen and an increased GGT. A fasting HbA1C >6.5 and a fasting glucose >120 is indicative of type 2 diabetes.
Insulin Resistance, Blood Sugar Imbalances & Diabetes
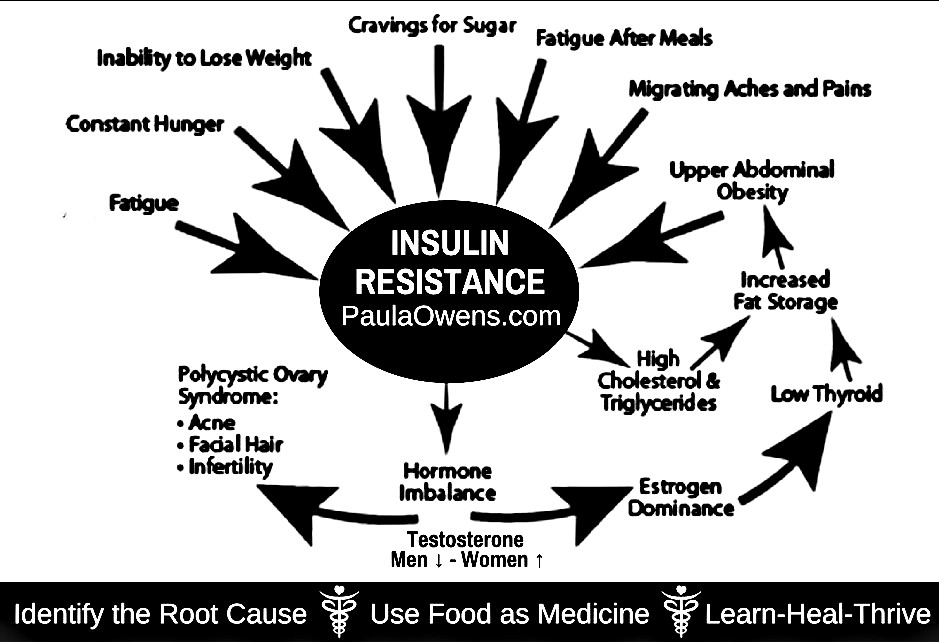
Symptoms and Conditions of Insulin Resistance
• Brain fog and an inability to focus
• Increased triglycerides, high LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol
• Excess belly fat and/or excess fat around the scapula
• Increased blood sugar (glucose), increase hemoglobin A1c, increased insulin, increased GGT, increased uric acid
• Extreme thirst, frequent urination
• Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
• Moodiness and emotional instability
• Poor memory, dementia, Alzheimer’s disease
• Hepatitis, underlying viral infections
• High blood sugar is inflammatory, which affects the immune system
• More infections than usual
• Very dry skin, sores that are slow to heal
• Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
• Gallbladder problems. Sticky, congested bile and difficulty digesting or metabolizing fats (when your body isn’t burning fats efficiently it puts more pressure on your sugar metabolism)
• High toxic load, exposure to too many chemicals, environmental toxicity
• Sleepiness, dizziness, fatigue
• Sugar and carb cravings; consuming more carbohydrates than your body can metabolize
External environmental toxins and internal endotoxin-producing bacterial toxins are major contributors linked to the diabetes epidemic.
Consequences of Insulin Resistance, Pre-diabetes and Diabetes
- An increased risk for dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (diabetes of the brain, a.k.a. Type 3 diabetes). Increased insulin doubles the risk for Alzheimer’s disease compared to those without diabetes. According to a study in the New England Journal of Medicine, even a mild elevation of blood sugar (105-110) is dramatically associated with an elevated risk for developing dementia.
- Chronic low level inflammation, which increases the risk for diabetes, Alzheimer’s, depression and many other diseases
- Obesity
- Damage to the eyes, kidneys, nerves, brain and heart.
- Major hormone disruption: insulin, glucagon, cortisol, estrogen dominance, thyroid dysfunction, low testosterone in men and high testosterone in women
- Accelerated aging
- Oxidation and mitochondrial damage
- Disrupted fat metabolism
- Brain shrinkage
- Increased risk of diabetes, dementia, fatty liver, PCOS, heart disease, hypertension, cancer, Alzheimer’s, obesity and other diseases.
High blood sugar drives the body into a fat storage mode rather than a fat burning mode. ALL hormones work in synergy with one another. The hormone you have the most control over is insulin. This is regulated by your diet, food quality, portion control, timing of meals, your environment, avoiding as many chemicals and toxins as possible, reducing toxic load, and what you choose to eat.
Root Causes of Insulin Resistance & Type 2 Diabetes
- Eating inflammatory foods! Carbohydrate overload and carbohydrate intolerance.
- Too many processed carbs, chemicals and excessive amounts of sugar, wheat, grains, fruit and fruit juice, fructose, soda and too much alcohol. Unbalanced meals that are heavy in processed carbohydrates, sugar, wheat and grains, gluten, high fructose corn syrup, excess omega-6 vegetable fats and rancid vegetable oils. Consuming fast food two or more times a week results on average an extra weight gain of 10 pounds and doubles the risk of prediabetes.
- Sleep deprivation, poor quality sleep, not enough rest
- GMOs, glyphosate, pesticides, herbicides, phthalates, plastics and other toxic chemicals and poisonous toxins in our food supply, water, the air we breathe, products we use in and around our homes, personal care products and the environment. These toxic chemicals bind to insulin receptor sites on the cells and block the cell receptors so they can’t respond to insulin, increasing risk of diabetes.
- Inflammation overload, which can be caused by any number of things including poor food choice, toxic overload, heavy metals, underlying infections, digestive distress, chronic and poorly managed stress, sedentary lifestyles, OTC and prescription medication use, and unhealthy lifestyle habits.
- Sedentary lifestyles
- Chronic dieting
- Statin drugs. Cholesterol-lowering statin drugs increase risk of developing type 2 diabetes by nearly 50 percent!
- Overfed and undernourished caused by poor food quality that is nutritionally-void, malabsorption and digestive issues.
- Disrupted circadian rhythms, lack of daily sunlight, excessive EMF exposure and exposure to blue light at night from smartphones and screens
- Elevated lypogenic (fat storing) enzymes and decreased lypolytic (fat burning) enzymes
- Emotional stress, adrenal dysfunction and altered hormonal levels. Years of chronic stress (emotional, mental, physical, environmental, and spiritual stress), adrenal dysfunction, high adrenaline and extremely low or elevated cortisol levels (which increase blood sugar).
The good news is that insulin resistance, pre-diabetes and diabetes are reversible! Find out how to reverse diabetes in part 2 of this article.
Read Part 2 •••►How to Reverse Diabetes Naturally
Wellness Videos
- Metformin Users Beware
- Are You Pre-Diabetic?
- Wellness Approach to Diabetes
- Do You Have High or Low Blood Sugar?
Related Posts
- Hormone Disrupting Chemicals: List of Endocrine Disruptors & Healthier Swaps
- Toxic Chemicals Harming Your Body, Brain, Hormones and Health

